printf("ho_tari\n");
PCA #7 본문
Kaggle의 레드와인의 질에 대한 데이터셋(Red Wine Quality | Kaggle)을 이용하여 다음의 실험을 진행하라. (즉 kaggle에서 notebook을 열어도 좋고, data를 다운로드 받아 google colab을 사용해도 좋음.) 다음의 조건들을 만족하도록 코드를 구성하고, 실험하도록 한다.
Perform the following experiment using the Kaggle's dataset on “the quality of red wine” (Red Wine Quality | Kaggle). You may open a notebook directly in kaggle, or user google colab with its downloaded data.) Write-down your own code to satisfy the following conditions.
1. Model
1) 3-hidden layers. Each hidden layers should have 512 neurons.
2) Adam Optimizer with MSE loss.
2. Data preparation
1) train set: the first 1000 samples.
2) test set: the left-overs.
3) min-max Normalization between 0 and 1 (hint. preprocessing.MinMaxScaler)
3. Learning parameters
1) validation: 20% hold-out CV
2) learning with 500 epochs (batch size: default)
4. Evaluation methods
1) Report the final MAE om training set, validation set, and test set
2) Show learning curves of MAE in training set and validation set in one graph
3) Compare the prediction results of the first 10 samples of the test set, with the true targets.
<코드>
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
df = pd.read_csv('winequality-red.csv')
train_df = df.iloc[:1000, :]
test_df = df.iloc[1000:, :]
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
train_df[train_df.columns] = scaler.fit_transform(train_df[train_df.columns])
test_df[test_df.columns] = scaler.fit_transform(test_df[test_df.columns])
train_df[train_df.columns[-1]] = scaler.fit_transform(train_df[train_df.columns[-1]].values.reshape(-1, 1))
test_df[test_df.columns[-1]] = scaler.fit_transform(test_df[test_df.columns[-1]].values.reshape(-1, 1))
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(train_df[train_df.columns[:-1]], train_df[train_df.columns[-1]], test_size=0.2)
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(512, activation='relu', input_shape=[len(X_train.columns)]))
model.add(Dense(512, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(512, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(1))
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='mse', metrics=['mae'])
history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, validation_data=(X_val, y_val), batch_size=32, epochs=500, verbose=1)
# Training set MAE
train_mae = model.evaluate(X_train, y_train, verbose=0)[1]
print('Training set MAE:', train_mae)
# Validation set MAE
val_mae = model.evaluate(X_val, y_val, verbose=0)[1]
print('Validation set MAE:', val_mae)
# Test set MAE
test_mae = model.evaluate(test_df[test_df.columns[:-1]], test_df[test_df.columns[-1]], verbose=0)[1]
print('Test set MAE:', test_mae)
plt.plot(history.history['mae'])
plt.plot(history.history['val_mae'])
plt.title('MAE')
plt.ylabel('MAE')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.legend(['Training set', 'Validation set'], loc='upper right')
plt.show()
predictions = model.predict(test_df[test_df.columns[:-1]])[:10]
print('Predictions:', predictions)
<learning curve in the training set & test set>

<the final MAE om training set, validation set, and test set>
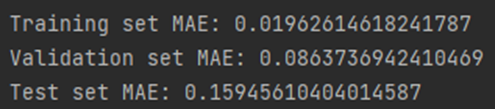
<the prediction results of the first 10 samples of the test set, (and compare it with the true targets>

Problem #3
Weight regularization을 시행해보자. 모든 Layer에 L1 regularization 0.001, L2 regularization 0.001을 적용하고, 다시 코드를 실행해보자. (다른 모든 조건은 동일하다.)
Apply Weight regularization, and re-run the code (set L1=0.001, L2=0.001 for all layers). Show your results in the same format.
<코드>
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
df = pd.read_csv('winequality-red.csv')
train_df = df.iloc[:1000]
test_df = df.iloc[1000:]
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
train_df[train_df.columns] = scaler.fit_transform(train_df[train_df.columns])
test_df[test_df.columns] = scaler.transform(test_df[test_df.columns])
train_df[train_df.columns[-1]] = scaler.fit_transform(train_df[train_df.columns[-1]].values.reshape(-1, 1))
test_df[test_df.columns[-1]] = scaler.transform(test_df[test_df.columns[-1]].values.reshape(-1, 1))
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(train_df[train_df.columns[:-1]], train_df[train_df.columns[-1]], test_size=0.2)
model = keras.Sequential([
layers.Dense(512, activation='relu', kernel_regularizer=keras.regularizers.l1_l2(l1=0.001, l2=0.001), input_shape=[len(X_train.columns)]),
layers.Dense(512, activation='relu', kernel_regularizer=keras.regularizers.l1_l2(l1=0.001, l2=0.001)),
layers.Dense(512, activation='relu', kernel_regularizer=keras.regularizers.l1_l2(l1=0.001, l2=0.001)),
layers.Dense(1)
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='mse', metrics=['mae'])
history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, validation_data=(X_val, y_val), batch_size=32, epochs=500, verbose=1)
# Training set MAE
train_mae = model.evaluate(X_train, y_train, verbose=0)[1]
print('Training set MAE:', train_mae)
# Validation set MAE
val_mae = model.evaluate(X_val, y_val, verbose=0)[1]
print('Validation set MAE:', val_mae)
# Test set MAE
test_mae = model.evaluate(test_df[test_df.columns[:-1]], test_df[test_df.columns[-1]], verbose=0)[1]
print('Test set MAE:', test_mae)
plt.plot(history.history['mae'])
plt.plot(history.history['val_mae'])
plt.title('MAE')
plt.ylabel('MAE')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.legend(['Training set', 'Validation set'], loc='upper right')
plt.show()
predictions = model.predict(test_df[test_df.columns[:-1]])[:10]
print('Predictions:', predictions)
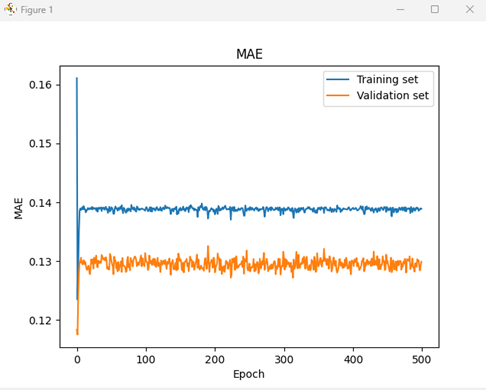
<learning curve in the training set & test set>
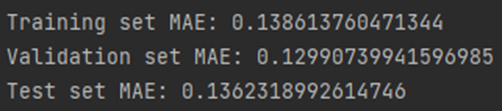
<the final MAE om training set, validation set, and test set>
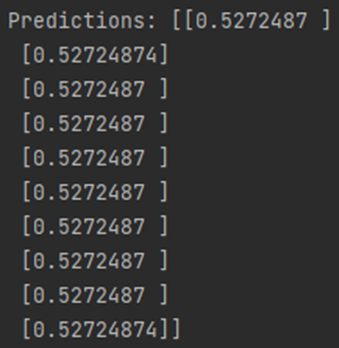
<the prediction results of the first 10 samples of the test set, (and compare it with the true targets>
Problem #4
위의 두 결과를 비교하고, 이유에 대해 설명해보아라. 특히 training set에서의 MAE이 어느 쪽이 더 우수하며, test set에서의 MAE는 어느쪽이 더 우수한지 설명해야하며, 왜 이러한 결과가 나타났는지 설명하여야 한다.
Compare the two results above and explain why the difference occurred. In particular, you should explain which one has better MAE in the training set and which one has better MAE in the test set, and explain why this happened.
Training set에서의 MAE를 비교해보면 weight regularization을 하기 전에는

으로 결과가 나오고 모든 layer에 L1 regularization 0.001, L2 regularization 0.001을 적용했을 때는

으로 결과가 나와 weight regularization을 하기 전에 MAE 값이 더 작게 나왔습니다.
Test set에서의 MAE를 비교해보면 weight regularization을 하기 전에는

으로 결과가 나오고 모든 layer에 L1 regularization 0.001, L2 regularization 0.001을 적용했을 때는

으로 결과가 나와 마찬가지로 weight regularization을 하기 전에 MAE 값이 더 작아 더 우수한 결과가 나온 것 같습니다.
Training set의 경우에는 l1_l2 regularization을 적용하지 않았을 때는 epoch이 진행될수록 MAE 값이 우하향하지만 중간에 몇 번 튀는 것을 그래프로 확인할 수 있습니다. l1_l2 regularization을 적용하였을 때는 MAE 값이 regularization을 적용하지 않았을 때보다는 컸지만 전체적으로 일정한 값을 유지하는 것을 그래프를 통해 확인할 수 있습니다. Final MAE 값을 보면 regularization 적용 전이 값이 더 크게 나오긴 했지만 epoch의 weight를 업데이트해주면서 overfitting을 막아주고 더 안정적인 학습을 할 수 있었던 것 같습니다.
Test set의 경우, l1_l2 regularization을 적용하지 않았을 때보다 적용하였을 때 MAE 값이 대략 2% 정도 낮게 나왔습니다.
Prediction 값들을 비교해보면 l1_l2 regularization을 적용하기 전에는 실제값에 따라 다 다르게 나왔지만 l1_l2 regularization을 적용한 후에는 모든 값들이 같게 나오는 결과를 볼 수 있습니다. Prediction 값들이 하나로 같은 것으로 보아 regression이 잘 된 것 같다고 생각하였습니다.




