printf("ho_tari\n");
ep.43 합성곱 신경망(CNN) 본문
2024.9.5
합성곱 신경망(CNN)
- 합성곱 신경망 CNN convolutional neural network
- 이미지 인식과 음성인식 등 다양한 곳에서 사용
- 특히 이미지 인식 분야에서 딥러닝을 활용한 기법은 거의 다 CNN을 기초로 한다.
전체 구조
완전연결 계층(Affine 계층)으로 이뤄진 네트워크의 예

- 완전연결 신경먕은 Affine 계층 활성화 함수를 갖는 ReLU 계층(혹은 Sigmoid 계층)이 이어집니다.
- 그림에서는 Affine-RuLU 조합이 4개가 쌓였고, 마지막 5번째 계층은 Affine 계층에 이어 소프트맥스 계층에서 최종 결과를 출력한다.
CNN으로 이뤄진 네트워크의 예 · 합성곱 계층과 풀링 계층이 새로 추가(회색)

합성곱 계층
합성곱 연산
합성곱 언산의 예 : 합성곱 연산을 @ 기호로 표기

합성곱 연산의 계산 순서

합성곱 연산의 편항 : 필터를 적용한 원소에 고정값(편항)을 더한다.

패딩
합성곱 연산의 패딩 처리 : 입력 데이터 주위에 0을 채운다(패딩은 점선으로 표시했으며 그 안의 값 '0'은 생 략했다).
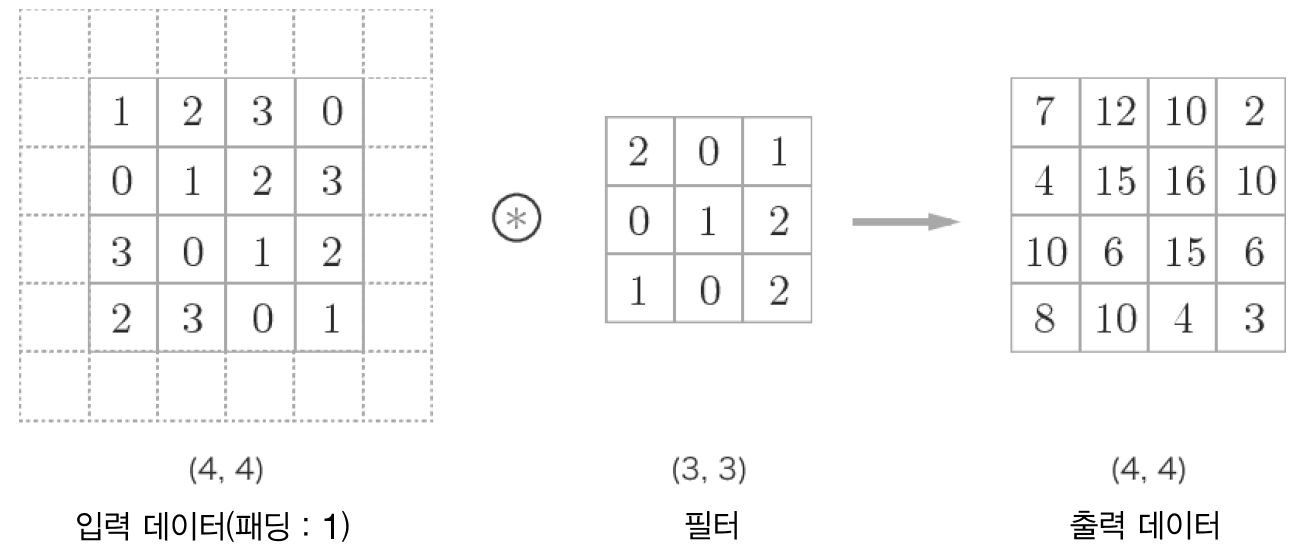
스트라이드
스트라이드가 2인 합성곱 연산

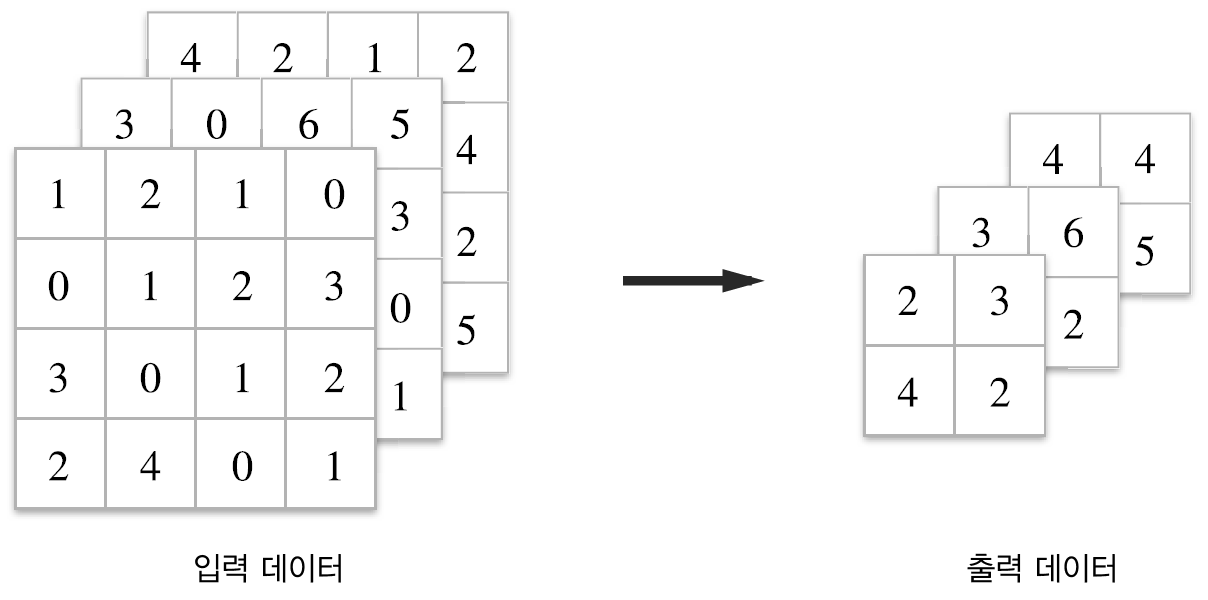
3차원 데이터의 합성곱 연산
3차원 데이터 합성곱 연산의 예

3차원 데이터 합성곱 연산의 계산 순서

블록으로 생각하기
합성곱 연산을 직육면체 블록으로 생각한다- 블록의 형상에 주의할 것!

여러 필터를 사용한 합성곱 연산의 예

합성곱 연산의 처리 흐름(편향 추가)

배치 처리
합성곱 연산의 처리 흐름(배치 처리)

폴링 계층
최대 풀링의 처리 순서

폴링 계층의 특징
- 학습해야 할 매개변수가 없다.
- 채널 수가 변하지 않는다.
풀링은 채널 수를 바꾸지 않는다.
- 입력의 변화에 영향을 적개 받는다.
입력 데이터가 가로로 1원소만큼 어긋나도 출력은 같다(데이터에 따라서는 다를 수도 있다).

합성곱/폴링 계층 구현하기
4차원 배열
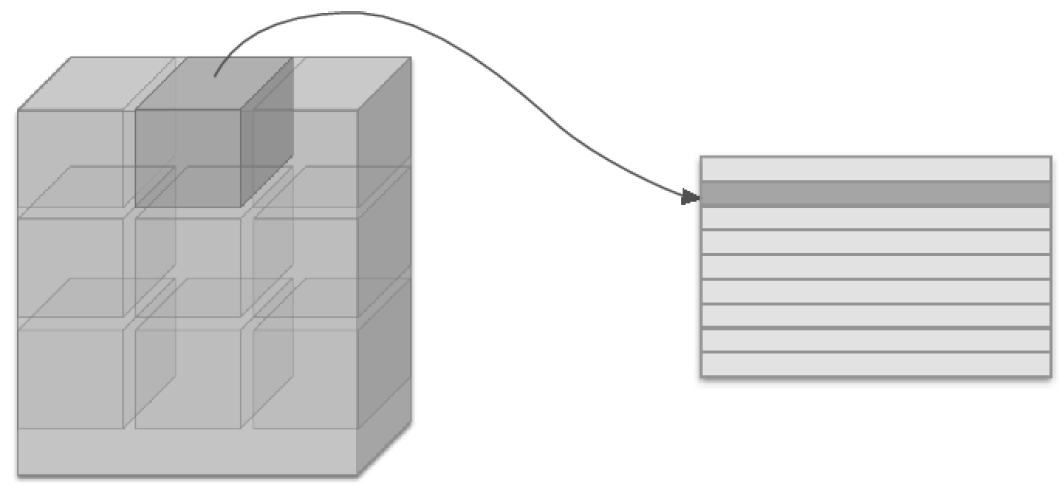
im2col로 데이터 전개하기
(대략적인)im2col의 동작
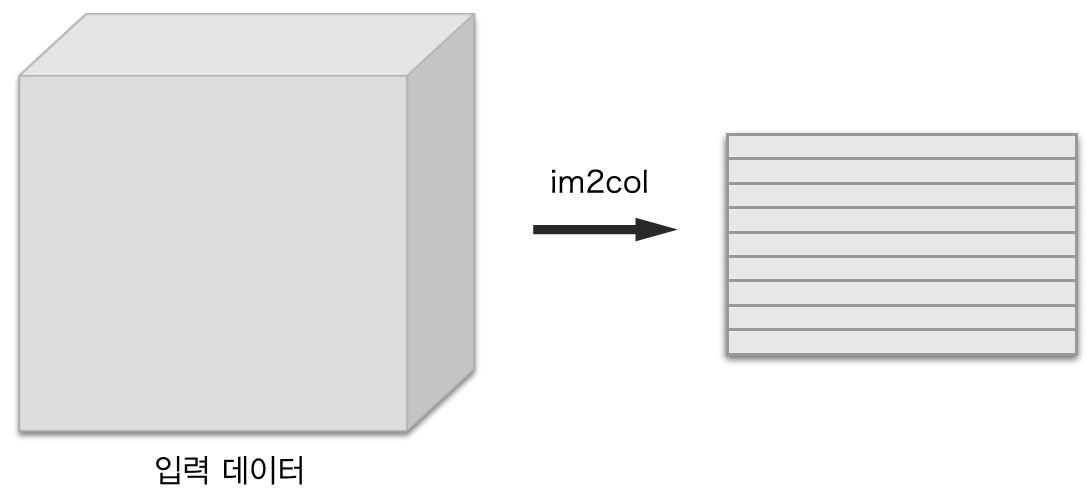
필터 적용 영역을 앞에서부터 순서대로 1줄로 펼친다.
합성곱 연산의 필터 처리 상세 과정 : 필터를 세로로 1열로 전개하고, im2col 이 전개한 데이터와 행렬 내적 을 계산합니다. 마지막으로 출력 데이터를 변형(reshape)합니다.

합성곱 계층 구현하기
넘파이의 transpose 함수로 축 순서 변경하기 : 인텍스(번호)로 축의 순서를 변경한다.

풀링계층 구현하기
입력 데이터에 풀링 적용 영역을 전개 (2X2 풀링의 예)

풀링 계층 구현의 흐름 : 풀링 적용 영역에서 가장큰 원소는 회색으로 표시

CNN 구현하기
단순한 CNN의 네트워크 구성

학습 전과 후의 1번째 층의 합성곱 계층의 가중치 : 가중치의 원소는 실수이지만, 이미지에서는 가장 작은 값(0)은 검은색,가장 큰 값(255)은 흰색으로 정규화하여 표시함
CNN 시각화하기
1번째 층의 가충치 시각화하기

가로 에지와 세로 에지에 반응하는 필터 : 출력 이미지 1은 세로 에지에 흰 픽셀이 나타나고,출력 이미지 2 는 가로 에지에 흰 픽셀이 많이 나온다.

층 깊이에 따른 추출 정보 변화
CNN의 합성곱 계층에서 추출되는 정보. 1번째 층은 에지와 블롭,3번째 층은 텍스처, 5번째 층은 시물의 일부, 마지막 완전연결 계층은 사물의 클래스(개, 자동차 등)에 뉴런이 반응한다.

대표적인 CNN
LeNet
LeNet의 구성

AlexNet
AlexNet의 구성

정리
import numpy as np
x=np.random.rand(10, 1, 28, 28)
x.shape
x[0].shape
x[1].shape
x[0,0].shape
#x[0,1].shape # index 1 is out of bounds for axis 1 with size 1
x[0,0] # 첫번째 데이터의 첫 채널의 공간 데이터
x=np.arange(0,10*1*28*28)
print(x)
x=np.arange(0,10*1*28*28).reshape(10, 1, 28, 28)
x[0, 0]



col[:, :, y, x, :, :] = img[:, :, y:y_max:stride, x:x_max:stride] 해석

filter y,x : 3 x 3
filter 0,0 인 곳은 3개임 : red 0,0 green 0,0 blue 0,0
red 0.0이 이동하면서 참여하는 영역을 out_h, out_w의 크기와 같다.
red 1 [[[[4 9 2 5 ] red 0 [[9 2 5 8 ] red -1 [[2 5 8 3]
(0 0) [5 6 2 4 ] (0 1) [6 2 4 0 ] (0 2) [2 4 0 3]
[2 4 5 4 ] [4 5 4 5 ] [5 4 5 2]
[5 6 5 4 ]] [6 5 4 7 ]] [5 4 7 8]]]
red 1 [[[5 6 2 4 ] red 0 [[6 2 4 0 ] red -1 [[2 4 0 3]
(1 0) [2 4 5 4 ] (1 1) [4 5 4 5 ] (1 2) [5 4 5 2]
[5 6 5 4 ] [6 5 4 7 ] [5 4 7 8]
[5 7 7 9 ]] [7 7 9 2 ]] [7 9 2 1]]]
red 1 [[[2 4 5 4 ] red 0 [[4 5 4 5 ] red -1 [[5 4 5 2]
(2 0) [5 6 5 4 ] (2 1) [6 5 4 7 ] (2 2) [5 4 7 8]
[5 7 7 9 ] [7 7 9 2 ] [7 9 2 1]
[5 8 5 3 ]] [8 5 3 8 ]] [5 8 8 4]]]]
# https://velog.io/@jadenkim5179/%EB%B0%91%EB%B0%94%EB%8B%A5-%EB%94%A5%EB%9F%AC%EB%8B%9D-im2col-%EA%B5%AC%ED%98%84-%EC%9D%B4%ED%95%B4%ED%95%98%EA%B8%B0
def im2col4test(input_data, filter_h, filter_w, stride=1, pad=0):
"""다수의 이미지를 입력받아 2차원 배열로 변환한다(평탄화).
Parameters
----------
input_data : 4차원 배열 형태의 입력 데이터(이미지 수, 채널 수, 높이, 너비)
filter_h : 필터의 높이
filter_w : 필터의 너비
stride : 스트라이드
pad : 패딩
Returns
-------
col : 2차원 배열
"""
#먼저 input_data.shape를 통해 데이터 수, 채널 수, 높이, 너비를 각각의 변수에 저장한다
#또한 공식을 통해서 output의 높이, 너비를 구한다
N, C, H, W = input_data.shape
out_h = (H + 2*pad - filter_h)//stride + 1
out_w = (W + 2*pad - filter_w)//stride + 1
# N C H W
img = np.pad(input_data, [(0,0), (0,0), (pad, pad), (pad, pad)], 'constant')
col = np.zeros((N, C, filter_h, filter_w, out_h, out_w))
print("col", col.shape)
for y in range(filter_h):
y_max = y + stride*out_h
for x in range(filter_w):
x_max = x + stride*out_w
print("col ==================")
print(col[:, :, y, x, :, :])
print("img ==================")
print(img[:, :, y:y_max:stride, x:x_max:stride])
col[:, :, y, x, :, :] = img[:, :, y:y_max:stride, x:x_max:stride]
print("col ==================")
print(col[:, :, y, x, :, :])
print("start", y, x)
print(col)
print("===========================")
print(col.transpose(0, 4, 5, 1, 2, 3))
col = col.transpose(0, 4, 5, 1, 2, 3).reshape(N*out_h*out_w, -1)
print("===========================")
print(col)
# (N, out_h, out_w, C, filter_h, filter_w)
# column N*out_h*out_w , -1 로 정렬
return col
#x1 = np.ones((2, 2, 3, 3)) # (데이터 수, 채널 수, 높이, 너비)
x1 = np.arange(1, 3*5*5+1).reshape(1, 3, 5, 5) # 4차원 배열
print(x1)
print("+++++++++++++++++++++++++++")
col1 = im2col4test(x1, 2, 2, stride=1, pad=0)
print("+++++++++++++++++++++++++++")
print(col1.shape) # (9, 75)
#x1 = np.ones((2, 2, 3, 3)) # (데이터 수, 채널 수, 높이, 너비)
x1 = np.arange(1, 37).reshape(2, 2, 3, 3) # 4차원 배열
print(x1)
print("+++++++++++++++++++++++++++")
col1 = im2col4test(x1, 2, 2, stride=1, pad=0)
print("+++++++++++++++++++++++++++")
print(col1.shape) # (9, 75)
'''
#x1 = np.random.rand(1, 3, 7, 7) # (데이터 수, 채널 수, 높이, 너비)
#x1 = np.zeros((1, 3, 4, 4)) # (데이터 수, 채널 수, 높이, 너비)
#x1 = np.ones((1, 3, 4, 4)) # (데이터 수, 채널 수, 높이, 너비)
#x1 = np.full((1, 3, 4, 4), 2) # (데이터 수, 채널 수, 높이, 너비)
x1 = np.ones((2, 2, 4, 4)) # (데이터 수, 채널 수, 높이, 너비)
print(x1)
#col1 = im2col4test(x1, 5, 5, stride=1, pad=0)
col1 = im2col4test(x1, 2, 2, stride=1, pad=0)
print(col1.shape) # (9, 75)
x2 = np.random.rand(10, 3, 7, 7) # 데이터 10개
np.ones_like(x2)
col2 = im2col4test(x2, 5, 5, stride=1, pad=0)
print(col2.shape) # (90, 75)
'''
def col2im4test(col, input_shape, filter_h, filter_w, stride=1, pad=0):
"""(im2col과 반대) 2차원 배열을 입력받아 다수의 이미지 묶음으로 변환한다.
Parameters
----------
col : 2차원 배열(입력 데이터)
input_shape : 원래 이미지 데이터의 형상(예:(10, 1, 28, 28))
filter_h : 필터의 높이
filter_w : 필터의 너비
stride : 스트라이드
pad : 패딩
Returns
-------
img : 변환된 이미지들
"""
N, C, H, W = input_shape
out_h = (H + 2*pad - filter_h)//stride + 1
out_w = (W + 2*pad - filter_w)//stride + 1
col = col.reshape(N, out_h, out_w, C, filter_h, filter_w).transpose(0, 3, 4, 5, 1, 2)
img = np.zeros((N, C, H + 2*pad + stride - 1, W + 2*pad + stride - 1))
for y in range(filter_h):
y_max = y + stride*out_h
for x in range(filter_w):
x_max = x + stride*out_w
img[:, :, y:y_max:stride, x:x_max:stride] += col[:, :, y, x, :, :]
#img[:, :, y:y_max:stride, x:x_max:stride] = col[:, :, y, x, :, :]
print("start", y, x)
print(img)
return img[:, :, pad:H + pad, pad:W + pad]
#dcol = np.arange(1, 65).reshape(8, 8) # 2차원 배열
#print(dcol)
col1 = im2col4test(x1, 2, 2, stride=1, pad=0)
#dx = col2im4test(dcol, (2, 2, 3, 3) self.x.shape, FH, FW, self.stride, self.pad)
#dx = col2im4test(dcol, (2, 2, 3, 3), 2, 2, stride=1, pad=0)
dx = col2im4test(col1, (2, 2, 3, 3), 2, 2, stride=1, pad=0)
print(dx.shape) # (2, 2, 3, 3)
print(dx)
CNN 기반 학습 code
def im2col(input_data, filter_h, filter_w, stride=1, pad=0):
"""다수의 이미지를 입력받아 2차원 배열로 변환한다(평탄화).
Parameters
----------
input_data : 4차원 배열 형태의 입력 데이터(이미지 수, 채널 수, 높이, 너비)
filter_h : 필터의 높이
filter_w : 필터의 너비
stride : 스트라이드
pad : 패딩
Returns
-------
col : 2차원 배열
"""
N, C, H, W = input_data.shape
out_h = (H + 2*pad - filter_h)//stride + 1
out_w = (W + 2*pad - filter_w)//stride + 1
img = np.pad(input_data, [(0,0), (0,0), (pad, pad), (pad, pad)], 'constant')
col = np.zeros((N, C, filter_h, filter_w, out_h, out_w))
for y in range(filter_h):
y_max = y + stride*out_h
for x in range(filter_w):
x_max = x + stride*out_w
col[:, :, y, x, :, :] = img[:, :, y:y_max:stride, x:x_max:stride]
col = col.transpose(0, 4, 5, 1, 2, 3).reshape(N*out_h*out_w, -1)
# (N, out_h, out_w, C, filter_h, filter_w)
# column N*out_h*out_w , -1 로 정렬
return col
class Convolution:
def __init__(self, W, b, stride=1, pad=0):
self.W = W
self.b = b
self.stride = stride
self.pad = pad
# 중간 데이터(backward 시 사용)
self.x = None
self.col = None
self.col_W = None
# 가중치와 편향 매개변수의 기울기
self.dW = None
self.db = None
def forward(self, x):
FN, C, FH, FW = self.W.shape
N, C, H, W = x.shape
out_h = 1 + int((H + 2*self.pad - FH) / self.stride)
out_w = 1 + int((W + 2*self.pad - FW) / self.stride)
col = im2col(x, FH, FW, self.stride, self.pad)
col_W = self.W.reshape(FN, -1).T
out = np.dot(col, col_W) + self.b
out = out.reshape(N, out_h, out_w, -1).transpose(0, 3, 1, 2)
self.x = x
self.col = col
self.col_W = col_W
return out
def backward(self, dout):
FN, C, FH, FW = self.W.shape
dout = dout.transpose(0,2,3,1).reshape(-1, FN)
self.db = np.sum(dout, axis=0)
self.dW = np.dot(self.col.T, dout)
self.dW = self.dW.transpose(1, 0).reshape(FN, C, FH, FW)
dcol = np.dot(dout, self.col_W.T)
dx = col2im(dcol, self.x.shape, FH, FW, self.stride, self.pad)
return dx
class Pooling:
def __init__(self, pool_h, pool_w, stride=1, pad=0):
self.pool_h = pool_h
self.pool_w = pool_w
self.stride = stride
self.pad = pad
self.x = None
self.arg_max = None
def forward(self, x):
N, C, H, W = x.shape
out_h = int(1 + (H - self.pool_h) / self.stride)
out_w = int(1 + (W - self.pool_w) / self.stride)
col = im2col(x, self.pool_h, self.pool_w, self.stride, self.pad)
col = col.reshape(-1, self.pool_h*self.pool_w)
arg_max = np.argmax(col, axis=1)
out = np.max(col, axis=1)
out = out.reshape(N, out_h, out_w, C).transpose(0, 3, 1, 2)
self.x = x
self.arg_max = arg_max
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dout = dout.transpose(0, 2, 3, 1)
pool_size = self.pool_h * self.pool_w
dmax = np.zeros((dout.size, pool_size))
dmax[np.arange(self.arg_max.size), self.arg_max.flatten()] = dout.flatten()
dmax = dmax.reshape(dout.shape + (pool_size,))
dcol = dmax.reshape(dmax.shape[0] * dmax.shape[1] * dmax.shape[2], -1)
dx = col2im(dcol, self.x.shape, self.pool_h, self.pool_w, self.stride, self.pad)
return dx
import sys, os
sys.path.append(os.pardir) # 부모 디렉터리의 파일을 가져올 수 있도록 설정
import pickle
import numpy as np
from collections import OrderedDict
#from common.layers import *
#from common.gradient import numerical_gradient
class SimpleConvNet:
"""단순한 합성곱 신경망
conv - relu - pool - affine - relu - affine - softmax
Parameters
----------
input_size : 입력 크기(MNIST의 경우엔 784)
hidden_size_list : 각 은닉층의 뉴런 수를 담은 리스트(e.g. [100, 100, 100])
output_size : 출력 크기(MNIST의 경우엔 10)
activation : 활성화 함수 - 'relu' 혹은 'sigmoid'
weight_init_std : 가중치의 표준편차 지정(e.g. 0.01)
'relu'나 'he'로 지정하면 'He 초깃값'으로 설정
'sigmoid'나 'xavier'로 지정하면 'Xavier 초깃값'으로 설정
"""
def __init__(self, input_dim=(1, 28, 28),
conv_param={'filter_num':30, 'filter_size':5, 'pad':0, 'stride':1},
hidden_size=100, output_size=10, weight_init_std=0.01):
filter_num = conv_param['filter_num']
filter_size = conv_param['filter_size']
filter_pad = conv_param['pad']
filter_stride = conv_param['stride']
input_size = input_dim[1]
conv_output_size = (input_size - filter_size + 2*filter_pad) / filter_stride + 1
pool_output_size = int(filter_num * (conv_output_size/2) * (conv_output_size/2))
# 가중치 초기화
self.params = {}
self.params['W1'] = weight_init_std * \
np.random.randn(filter_num, input_dim[0], filter_size, filter_size)
self.params['b1'] = np.zeros(filter_num)
self.params['W2'] = weight_init_std * \
np.random.randn(pool_output_size, hidden_size)
self.params['b2'] = np.zeros(hidden_size)
self.params['W3'] = weight_init_std * \
np.random.randn(hidden_size, output_size)
self.params['b3'] = np.zeros(output_size)
# 계층 생성
self.layers = OrderedDict()
self.layers['Conv1'] = Convolution(self.params['W1'], self.params['b1'],
conv_param['stride'], conv_param['pad'])
self.layers['Relu1'] = Relu()
self.layers['Pool1'] = Pooling(pool_h=2, pool_w=2, stride=2)
self.layers['Affine1'] = Affine(self.params['W2'], self.params['b2'])
self.layers['Relu2'] = Relu()
self.layers['Affine2'] = Affine(self.params['W3'], self.params['b3'])
self.last_layer = SoftmaxWithLoss()
def predict(self, x):
for layer in self.layers.values():
x = layer.forward(x)
return x
def loss(self, x, t):
"""손실 함수를 구한다.
Parameters
----------
x : 입력 데이터
t : 정답 레이블
"""
y = self.predict(x)
return self.last_layer.forward(y, t)
def accuracy(self, x, t, batch_size=100):
if t.ndim != 1 : t = np.argmax(t, axis=1)
acc = 0.0
for i in range(int(x.shape[0] / batch_size)):
tx = x[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size]
tt = t[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size]
y = self.predict(tx)
y = np.argmax(y, axis=1)
acc += np.sum(y == tt)
return acc / x.shape[0]
def numerical_gradient(self, x, t):
"""기울기를 구한다(수치미분).
Parameters
----------
x : 입력 데이터
t : 정답 레이블
Returns
-------
각 층의 기울기를 담은 사전(dictionary) 변수
grads['W1']、grads['W2']、... 각 층의 가중치
grads['b1']、grads['b2']、... 각 층의 편향
"""
loss_w = lambda w: self.loss(x, t)
grads = {}
for idx in (1, 2, 3):
grads['W' + str(idx)] = numerical_gradient(loss_w, self.params['W' + str(idx)])
grads['b' + str(idx)] = numerical_gradient(loss_w, self.params['b' + str(idx)])
return grads
def gradient(self, x, t):
"""기울기를 구한다(오차역전파법).
Parameters
----------
x : 입력 데이터
t : 정답 레이블
Returns
-------
각 층의 기울기를 담은 사전(dictionary) 변수
grads['W1']、grads['W2']、... 각 층의 가중치
grads['b1']、grads['b2']、... 각 층의 편향
"""
# forward
self.loss(x, t)
# backward
dout = 1
dout = self.last_layer.backward(dout)
layers = list(self.layers.values())
layers.reverse()
for layer in layers:
dout = layer.backward(dout)
# 결과 저장
grads = {}
grads['W1'], grads['b1'] = self.layers['Conv1'].dW, self.layers['Conv1'].db
grads['W2'], grads['b2'] = self.layers['Affine1'].dW, self.layers['Affine1'].db
grads['W3'], grads['b3'] = self.layers['Affine2'].dW, self.layers['Affine2'].db
return grads
def save_params(self, file_name="params.pkl"):
params = {}
for key, val in self.params.items():
params[key] = val
with open(file_name, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(params, f)
def load_params(self, file_name="params.pkl"):
with open(file_name, 'rb') as f:
params = pickle.load(f)
for key, val in params.items():
self.params[key] = val
for i, key in enumerate(['Conv1', 'Affine1', 'Affine2']):
self.layers[key].W = self.params['W' + str(i+1)]
self.layers[key].b = self.params['b' + str(i+1)]
def predict(self, x):
for layer in self.layers.values():
x = layer.forward(x)
return x
def loss(self, x, t):
"""손실 함수를 구한다.
Parameters
----------
x : 입력 데이터
t : 정답 레이블
"""
y = self.predict(x)
return self.last_layer.forward(y, t)
def gradient(self, x, t):
"""기울기를 구한다(오차역전파법).
Parameters
----------
x : 입력 데이터
t : 정답 레이블
Returns
-------
각 층의 기울기를 담은 사전(dictionary) 변수
grads['W1']、grads['W2']、... 각 층의 가중치
grads['b1']、grads['b2']、... 각 층의 편향
"""
# forward
self.loss(x, t)
# backward
dout = 1
dout = self.last_layer.backward(dout)
layers = list(self.layers.values())
layers.reverse()
for layer in layers:
dout = layer.backward(dout)
# 결과 저장
grads = {}
grads['W1'], grads['b1'] = self.layers['Conv1'].dW, self.layers['Conv1'].db
grads['W2'], grads['b2'] = self.layers['Affine1'].dW, self.layers['Affine1'].db
grads['W3'], grads['b3'] = self.layers['Affine2'].dW, self.layers['Affine2'].db
return grads
class Relu:
def __init__(self):
self.mask = None
def forward(self, x):
self.mask = (x <= 0)
out = x.copy()
out[self.mask] = 0
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dout[self.mask] = 0
dx = dout
return dx
class Affine:
def __init__(self, W, b):
self.W = W
self.b = b
self.x = None
self.original_x_shape = None
# 가중치와 편향 매개변수의 미분
self.dW = None
self.db = None
def forward(self, x):
# 텐서 대응
self.original_x_shape = x.shape
x = x.reshape(x.shape[0], -1)
self.x = x
out = np.dot(self.x, self.W) + self.b
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dx = np.dot(dout, self.W.T)
self.dW = np.dot(self.x.T, dout)
self.db = np.sum(dout, axis=0)
dx = dx.reshape(*self.original_x_shape) # 입력 데이터 모양 변경(텐서 대응)
return dx
class SoftmaxWithLoss:
def __init__(self):
self.loss = None # 손실함수
self.y = None # softmax의 출력
self.t = None # 정답 레이블(원-핫 인코딩 형태)
def forward(self, x, t):
self.t = t
self.y = softmax(x)
self.loss = cross_entropy_error(self.y, self.t)
return self.loss
def backward(self, dout=1):
batch_size = self.t.shape[0]
if self.t.size == self.y.size: # 정답 레이블이 원-핫 인코딩 형태일 때
dx = (self.y - self.t) / batch_size
else:
dx = self.y.copy()
dx[np.arange(batch_size), self.t] -= 1
dx = dx / batch_size
return dx
class Trainer:
"""신경망 훈련을 대신 해주는 클래스
"""
def __init__(self, network, x_train, t_train, x_test, t_test,
epochs=20, mini_batch_size=100,
optimizer='SGD', optimizer_param={'lr':0.01},
evaluate_sample_num_per_epoch=None, verbose=True):
self.network = network
self.verbose = verbose
self.x_train = x_train
self.t_train = t_train
self.x_test = x_test
self.t_test = t_test
self.epochs = epochs
self.batch_size = mini_batch_size
self.evaluate_sample_num_per_epoch = evaluate_sample_num_per_epoch
# optimzer
optimizer_class_dict = {'sgd':SGD, 'momentum':Momentum, 'nesterov':Nesterov,
'adagrad':AdaGrad, 'rmsprpo':RMSprop, 'adam':Adam}
self.optimizer = optimizer_class_dict[optimizer.lower()](**optimizer_param)
self.train_size = x_train.shape[0]
self.iter_per_epoch = max(self.train_size / mini_batch_size, 1)
self.max_iter = int(epochs * self.iter_per_epoch)
self.current_iter = 0
self.current_epoch = 0
self.train_loss_list = []
self.train_acc_list = []
self.test_acc_list = []
def train_step(self):
batch_mask = np.random.choice(self.train_size, self.batch_size)
x_batch = self.x_train[batch_mask]
t_batch = self.t_train[batch_mask]
grads = self.network.gradient(x_batch, t_batch)
self.optimizer.update(self.network.params, grads)
loss = self.network.loss(x_batch, t_batch)
self.train_loss_list.append(loss)
if self.verbose: print("train loss:" + str(loss))
if self.current_iter % self.iter_per_epoch == 0:
self.current_epoch += 1
x_train_sample, t_train_sample = self.x_train, self.t_train
x_test_sample, t_test_sample = self.x_test, self.t_test
if not self.evaluate_sample_num_per_epoch is None:
t = self.evaluate_sample_num_per_epoch
x_train_sample, t_train_sample = self.x_train[:t], self.t_train[:t]
x_test_sample, t_test_sample = self.x_test[:t], self.t_test[:t]
train_acc = self.network.accuracy(x_train_sample, t_train_sample)
test_acc = self.network.accuracy(x_test_sample, t_test_sample)
self.train_acc_list.append(train_acc)
self.test_acc_list.append(test_acc)
if self.verbose: print("=== epoch:" + str(self.current_epoch) + ", train acc:" + str(train_acc) + ", test acc:" + str(test_acc) + " ===")
self.current_iter += 1
def train(self):
for i in range(self.max_iter):
self.train_step()
test_acc = self.network.accuracy(self.x_test, self.t_test)
if self.verbose:
print("=============== Final Test Accuracy ===============")
print("test acc:" + str(test_acc))
class SGD:
"""확률적 경사 하강법(Stochastic Gradient Descent)"""
def __init__(self, lr=0.001):
self.lr = lr
#params = 가중치 / grads = 기울기
def update(self, params, grads):
for key in params.keys():
params[key] -= self.lr * grads[key]
class Momentum:
"""모멘텀 SGD"""
def __init__(self, lr=0.001, momentum=0.9):
self.lr = lr
self.momentum = momentum
self.v = None
# v는 초기화x , update 호출시 매개변수와 같은 구조의 데이터 딕셔너리로 저장
def update(self, params, grads):
if self.v is None:
self.v = {}
for key, val in params.items():
self.v[key] = np.zeros_like(val)
for key in params.keys():
self.v[key] = self.momentum*self.v[key] - self.lr*grads[key]
params[key] += self.v[key]
class Nesterov:
"""Nesterov's Accelerated Gradient (http://arxiv.org/abs/1212.0901)"""
# NAG는 모멘텀에서 한 단계 발전한 방법이다. (http://newsight.tistory.com/224)
def __init__(self, lr=0.01, momentum=0.9):
self.lr = lr
self.momentum = momentum
self.v = None
def update(self, params, grads):
if self.v is None:
self.v = {}
for key, val in params.items():
self.v[key] = np.zeros_like(val)
for key in params.keys():
self.v[key] *= self.momentum
self.v[key] -= self.lr * grads[key]
params[key] += self.momentum * self.momentum * self.v[key]
params[key] -= (1 + self.momentum) * self.lr * grads[key]
class RMSprop:
"""RMSprop"""
def __init__(self, lr=0.01, decay_rate = 0.99):
self.lr = lr
self.decay_rate = decay_rate
self.h = None
def update(self, params, grads):
if self.h is None:
self.h = {}
for key, val in params.items():
self.h[key] = np.zeros_like(val)
for key in params.keys():
self.h[key] *= self.decay_rate
self.h[key] += (1 - self.decay_rate) * grads[key] * grads[key]
params[key] -= self.lr * grads[key] / (np.sqrt(self.h[key]) + 1e-7)
class AdaGrad:
"""AdaGrad"""
def __init__(self, lr=0.01):
self.lr = lr
self.h = None
def update(self, params, grads):
if self.h is None:
self.h = {}
for key, val in params.items():
self.h[key] = np.zeros_like(val)
for key in params.keys():
self.h[key] += grads[key] * grads[key]
params[key] -= self.lr * grads[key] / (np.sqrt(self.h[key]) + 1e-7)
# 1e-7 은 0으로 나누지 않게하는 값
class Adam:
"""Adam (http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980v8)"""
def __init__(self, lr=0.001, beta1=0.9, beta2=0.999):
self.lr = lr
self.beta1 = beta1
self.beta2 = beta2
self.iter = 0
self.m = None
self.v = None
def update(self, params, grads):
if self.m is None:
self.m, self.v = {}, {}
for key, val in params.items():
self.m[key] = np.zeros_like(val)
self.v[key] = np.zeros_like(val)
self.iter += 1
lr_t = self.lr * np.sqrt(1.0 - self.beta2**self.iter) / (1.0 - self.beta1**self.iter)
for key in params.keys():
#self.m[key] = self.beta1*self.m[key] + (1-self.beta1)*grads[key]
#self.v[key] = self.beta2*self.v[key] + (1-self.beta2)*(grads[key]**2)
self.m[key] += (1 - self.beta1) * (grads[key] - self.m[key])
self.v[key] += (1 - self.beta2) * (grads[key]**2 - self.v[key])
params[key] -= lr_t * self.m[key] / (np.sqrt(self.v[key]) + 1e-7)
#unbias_m += (1 - self.beta1) * (grads[key] - self.m[key]) # correct bias
#unbisa_b += (1 - self.beta2) * (grads[key]*grads[key] - self.v[key]) # correct bias
#params[key] += self.lr * unbias_m / (np.sqrt(unbisa_b) + 1e-7)
def softmax(x):
if x.ndim == 2:
x = x.T
x = x - np.max(x, axis=0)
y = np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x), axis=0)
return y.T
x = x - np.max(x) # 오버플로 대책
return np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x))
def cross_entropy_error(y, t):
if y.ndim == 1:
t = t.reshape(1, t.size)
y = y.reshape(1, y.size)
# 훈련 데이터가 원-핫 벡터라면 정답 레이블의 인덱스로 반환
if t.size == y.size:
t = t.argmax(axis=1)
batch_size = y.shape[0]
return -np.sum(np.log(y[np.arange(batch_size), t] + 1e-7)) / batch_size
def col2im(col, input_shape, filter_h, filter_w, stride=1, pad=0):
"""(im2col과 반대) 2차원 배열을 입력받아 다수의 이미지 묶음으로 변환한다.
Parameters
----------
col : 2차원 배열(입력 데이터)
input_shape : 원래 이미지 데이터의 형상(예:(10, 1, 28, 28))
filter_h : 필터의 높이
filter_w : 필터의 너비
stride : 스트라이드
pad : 패딩
Returns
-------
img : 변환된 이미지들
"""
N, C, H, W = input_shape
out_h = (H + 2*pad - filter_h)//stride + 1
out_w = (W + 2*pad - filter_w)//stride + 1
col = col.reshape(N, out_h, out_w, C, filter_h, filter_w).transpose(0, 3, 4, 5, 1, 2)
img = np.zeros((N, C, H + 2*pad + stride - 1, W + 2*pad + stride - 1))
for y in range(filter_h):
y_max = y + stride*out_h
for x in range(filter_w):
x_max = x + stride*out_w
img[:, :, y:y_max:stride, x:x_max:stride] += col[:, :, y, x, :, :]
return img[:, :, pad:H + pad, pad:W + pad]
# coding: utf-8
import sys, os
sys.path.append(os.pardir) # 부모 디렉터리의 파일을 가져올 수 있도록 설정
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#from dataset.mnist import load_mnist
#from simple_convnet import SimpleConvNet
#from common.trainer import Trainer
# 데이터 읽기
#(x_train, t_train), (x_test, t_test) = load_mnist(flatten=False)
import tensorflow as tf
(x_train,t_train),(x_test,t_test) = tf.keras.datasets.mnist.load_data()
x_test = x_test / 255
x_train = x_train / 255
x_train = x_train.reshape(x_train.shape[0], 1, 28, 28)
x_test = x_test.reshape(x_test.shape[0], 1, 28, 28)
# one hot encode y data
#y_train = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train, 10)
#y_test = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test, 10)
# 시간이 오래 걸릴 경우 데이터를 줄인다.
#x_train, t_train = x_train[:5000], t_train[:5000]
#x_test, t_test = x_test[:1000], t_test[:1000]
max_epochs = 20
network = SimpleConvNet(input_dim=(1,28,28),
conv_param = {'filter_num': 30, 'filter_size': 5, 'pad': 0, 'stride': 1},
hidden_size=100, output_size=10, weight_init_std=0.01)
trainer = Trainer(network, x_train, t_train, x_test, t_test,
epochs=max_epochs, mini_batch_size=100,
optimizer='Adam', optimizer_param={'lr': 0.001},
evaluate_sample_num_per_epoch=1000)
trainer.train()
# 매개변수 보존
network.save_params("params.pkl")
print("Saved Network Parameters!")
# 그래프 그리기
markers = {'train': 'o', 'test': 's'}
x = np.arange(max_epochs)
plt.plot(x, trainer.train_acc_list, marker='o', label='train', markevery=2)
plt.plot(x, trainer.test_acc_list, marker='s', label='test', markevery=2)
plt.xlabel("epochs")
plt.ylabel("accuracy")
plt.ylim(0, 1.0)
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.show()
출력 3 x 3 2개


'두산로보틱스 ROKEY 부트 캠프 > Computer Vision 교육' 카테고리의 다른 글
| ep.45 인공신경망(Artificial Neural Network) (0) | 2024.09.09 |
|---|---|
| ep.44 딥러닝 (0) | 2024.09.06 |
| ep.42 학습관련기술들 (0) | 2024.09.04 |
| ep.41 신경망학습, 오차역전파법 (0) | 2024.09.03 |
| ep.40 퍼셉트론, 신경망 (0) | 2024.09.02 |





