printf("ho_tari\n");
Array (array 클래스) 본문
<main.cpp>
#include <iostream>
#include "array.h"
int main()
{
std::cout << "Array::ARRAYSIZE : " << Array::getDefaultSize() << std::endl;
Array arr1;
Array arr2(100);
int nums[] = {1,2,3,4,5};
Array arr3(nums,5);
const Array arr4 = arr3;
arr1 = arr4;
if (arr1 == arr4)
{
std::cout << "arr1 and arr4 are equal" << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << "arr1 and arr4 are not equal" << std::endl;
}
arr1[0] = arr1[4];
for (int i = 0; i<arr1.size(); ++i)
{
std::cout << arr1[i] << " "; //arr1.operator[](i)
}
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}
<array.h>
#ifndef ARRAY_H
#define ARRAY_H
//extern const int ARRAYSIZE; //main.cpp에서 다른 파일의 전역변수에 접근할 때는 extern을 써줘야한다.
class Array {
private:
static const int ARRAYSIZE;
// 전역변수이지만 class와 관련된 전역변수는 static으로 써 클래스 안에 둘 수 있다.
//private에 두면 main에서는 접근불가능
//public에 두면 main에서 접근가능
int *pArr_;
int size_;
public:
//Array *operator&() const {return this;}
//const Array *operator&() const {return this;}
static int getDefaultSize(); // static이 붙었기 때문에 멤버함수가 아니라 전역함수이다.
//Array();
explicit Array(int size = ARRAYSIZE);
//인자가 1개있는 생성자에서 explicit을 쓰면 명시적으로 설정해주면 Array arr = 100; 처럼 배열을 생성할 수 없다.
//반드시 Array arr(100);의 형태로 써야한다.
Array(const Array& rhs);
Array(const int *pArr, int size);
~Array();
Array& operator=(const Array& rhs);
bool operator==(const Array& rhs) const;
int& operator[](int index);
const int& operator[](int index) const;
int size() const;
};
#endif
<array.cpp>
#include <cassert>
#include "array.h"
//const int ARRAYSIZE = 100; //constant (vs. literal)
const int Array::ARRAYSIZE = 100;
/*Array::Array()
:pArr_(new int[ARRAYSIZE]),size_(ARRAYSIZE) //생성자 초기화 리스트 (콜론을 사용해 표시)- 생성자에서만 쓸 수 있음
{
//pArr_ = new int[ARRAYSIZE];
assert(pArr_);
//size_ = ARRAYSIZE;
}
*/
int Array::getDefaultSize()
{
return Array::ARRAYSIZE;
}
Array::Array(int size)
: pArr_(new int[size]),size_(size)
{
//pArr_ = new int[size];
assert(pArr_);
//size_ = size;
}
Array::Array(const Array& rhs)
:pArr_(new int[rhs.size_]),size_(rhs.size_)
{
//pArr_ = new int[rhs.size_];
assert(pArr_);
//size_ = rhs.size_;
for (int i = 0; i<rhs.size(); i++)
{
pArr_[i] = rhs.pArr_[i];
}
}
Array::Array(const int *pArr,int size)
:pArr_(new int[size]),size_(size)
{
//pArr_ = new int[size];
assert(pArr_);
//size_ = size;
for (int i = 0; i<size; ++i)
{
pArr_[i] = pArr[i];
}
}
Array::~Array()
{
delete[] pArr_;
}
Array& Array::operator=(const Array& rhs)
{
if (this != &rhs)
{
delete[] pArr_;
pArr_ = new int[rhs.size_];
assert(pArr_);
size_ = rhs.size_;
for (int i = 0; i<rhs.size_; ++i)
{
pArr_[i] = rhs.pArr_[i];
}
}
return *this;
}
bool Array::operator==(const Array& rhs) const
{
if (size_ != rhs.size_)
return false;
int i;
for (i = 0; i<rhs.size_; ++i)
{
if (pArr_[i] != rhs.pArr_[i])
{
break;
}
}
return (i == rhs.size_);
}
int& Array::operator[](int index)
{
return pArr_[index];
}
const int& Array::operator[](int index)const
{
return pArr_[index];
}
int Array::size() const
{
return size_;
}
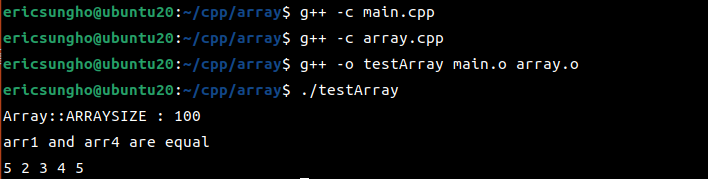
<compile 결과>
'C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Queue2 (생성자 초기화 리스트, static member, explicit) (0) | 2023.09.07 |
|---|---|
| Stack2 (extern, explicit) (0) | 2023.09.07 |
| Linked List (0) | 2023.09.05 |
| String (클래스 개선) (0) | 2023.09.05 |
| StringRep (reference counting 참조 계수) (0) | 2023.09.05 |




